Special case of amalgam fillings
Fillings with amalgam - curse or blessing?
Even today, millions of teeth around the world still have amalgam fillings - a mixture of around 60% silver, 40% mercury and various other heavy metals such as copper and tin.
Like all plastic filling materials - i.e. materials that are inserted softly into the tooth and only harden there - amalgam does not remain stable in the long term, but is subject to various changes in the mouth. In the case of amalgam, corrosion is the main cause, which can lead to leaking filling edges, the ingress of bacteria and, as a result, to renewed caries ("secondary caries"). It is also common for entire tooth walls or cusps to break off due to stresses in the tooth. Nevertheless, with an average service life of 9 - 20 years (in individual cases even up to 30 years), it still has the longest durability compared to other plastic filling materials such as plastics.
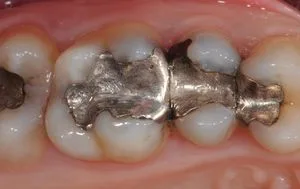
Due to the health concerns about its ingredient mercury, amalgam only plays a minor role and is therefore no longer used in our practice!

In particular, people who have several different metals in their mouth (such as gold and amalgam) have increased mercury levels in their body, as mercury ions can be released from the amalgam due to electrochemical corrosion (battery effect) in the mouth. In addition to mercury, other heavy metals such as copper or tin also enter the body through abrasion (abrasion of the teeth under function) and are deposited primarily in fatty and nerve tissue. This is where they can develop their neurotoxic effect.
Amalgam can trigger many secondary diseases, which can break out sooner or later depending on the physical condition or degree of exposure. In particular, many chronic and initially almost imperceptible illnesses are attributed to amalgam.
Allergies, immune deficiency, anemia, depression, asthma, headaches, anxiety, intestinal diseases, skin eczema, neurodermatitis, memory disorders, joint pain, cardiac arrhythmia, liver and kidney damage and much more.
Dr. Jens Tartsch

